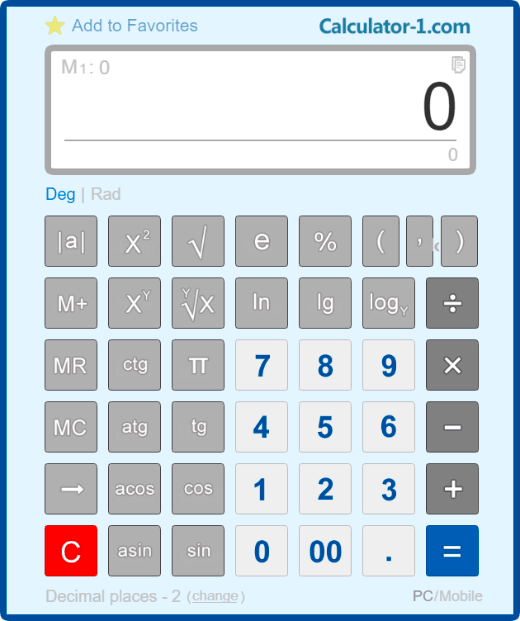

A scientific calculator supports calculations of trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, etc. Using this calculator, you can find the logarithm of a number, raise a number to a power, find a square root and even an nth root.
A scientific calculator is easy to use online - there is no need to download or install it on your PC or laptop.
For any calculation, you can use either a mouse or a numpad.
Moreover, you can customize the settings of the calculator and save them.
Below you can find examples and information on how to use a scientific calculator.
[ sin ] - calculates sine of an angle;
[ cos ] - calculates cosine of an angle;
[ tg ] - calculates tangent of an angle;
[ ctg ] - calculates cotangent of an angle;
[ π ] - is a mathematical constant, the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter;
[ e ] - is a mathematical constant, Euler's number;
[ log ] - is the common logarithm;
[ ln ] - is the natural logarithm (to the base e);
[ logY ] - is the logarithm of X to the base Y;
[ √ ] - calculates the square root;
[ X2 ] - raises X to the power of 2;
[ XY ] - raises X to the power of Y.
[ 0 ], [ 1 ], [ 2 ], ... [ 9 ] - standard number keys;
[ 00 ] - inputs two zeros;
[ → ] - deletes the last character entered on the display;
[ +/- ] - changes the mathematical sign of the displayed number to the opposite one;
[ + ] - addition, [ - ] - subtraction, [ × ] - multiplication, [ ÷ ] - division;
[ % ] - calculates percentages;
[ M+ ] - saves the number to memory with the [ + ] sign;
[ M- ] - saves the number to memory with the [ - ] sign;
[ MR ] - displays the memory content;
[ MC ] - erases the memory content;
[ AC ] - resets the calculator and clears the current memory cell;
[ C ] - resets the calculator without resetting the memory.
The calculator supports input from any numeric keys of a computer keyboard: both the numeric keys at the top and the separate numeric keypad on the right.
You can use the [Enter] key to enter the equal character.
To delete the last character, press the [Backspace] key.
To enter a plus sign, use the [ + ] key at the top or on the numeric keypad.
To enter a minus sign, use the [ - ] key at the top or on the numeric keypad.
Use the [ * ] key on the numeric keypad to enter the multiplication sign.
Use the [ / ] key on the numeric keypad to enter the division sign.
You can use the [Esc] and [Del] keys on the main keyboard, or the [End] key on the numeric keypad to reset the calculator.
Tangent of a 45 degrees angle: 45 [ tg ]. The result is 1.
Sine of a 30 degrees angle: 30 [ sin ]. The result is 0.5.
The common logarithm of 100: 100 [ log ]. The result is 2.
The logarithm of 125 to the base 5: 125 [ logY ] 5. The result is 3.
Calculating the square root of 529: 529 [ √ ]. The result is 23.
Raising 3 to the power of 4: 3 [ XY ] 4 [ = ]. The result is 81.
Calculating a percentage of a number: 500 [ × ] 25 [ % ]. The result is 125.
Calculating what percentage one number is of another: 25 [ ÷ ] 500 [ % ]. The result is 5%.
Adding a percentage to a number: 500 [ + ] 25 [ % ]. The result is 625.
Subtracting a percentage from a number: 500 [ - ] 25 [ % ]. The result is 375.
The direct predecessor of a calculator is a mechanical and portable counting machine called arithmometer. It was primarily used for multiplication and division. Though it is possible to use an arithmometer for addition or subtraction, it is quite difficult to do. Based on its working principle, the predecessor of a calculator is a digital device, that is why the result of calculation is always one hundred percent correct.